Page 283 - Ghidul Serviciilor Medicale Synevo, Ediția 1
P. 283
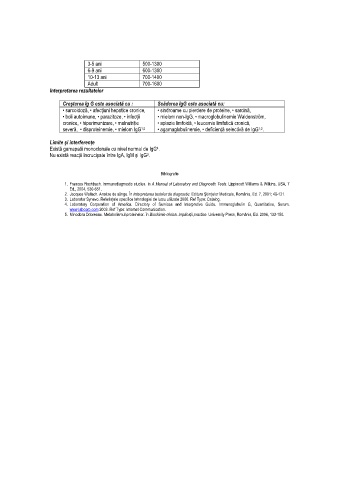
3-5 ani 500-1300
6-9 ani 600-1300
10-13 ani 700-1400
Adult 700-1600
Interpretarea rezultatelor
Creşterea Ig G este asociată cu : Scăderea IgG este asociată cu:
• sarcoidoză, • afecŃiuni hepatice cronice, • sindroame cu pierdere de proteine, • sarcină,
• boli autoimune, • parazitoze, • infecŃii • mielom non-IgG, • macroglobulinemie Waldenström,
cronice, • hiperimunizare, • malnutriŃie • aplazie limfoidă, • leucemie limfatică cronică,
1;2
1;2
severă, • disproteinemie, • mielom IgG • agamaglobulinemie, • deficienŃă selectivă de IgG .
Limite şi interferenŃe
4
Există gamapatii monoclonale cu nivel normal de IgG .
Nu există reacŃii încrucişate între IgA, IgM şi IgG .
3
Bibliografie
1. Frances Fischbach. Immunodiagnostic studies. In A Manual of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, USA, 7
Ed., 2004, 530-651.
2. Jacques Wallach. Analize de sânge. În Interpretarea testelor de diagnostic. Editura ŞtiinŃelor Medicale, România, Ed. 7, 2001; 49-121.
3. Laborator Synevo. ReferinŃele specifice tehnologiei de lucru utilizate 2006. Ref Type: Catalog.
4. Laboratory Corporation of America. Directory of Services and Interpretive Guide. Immunoglobulin G, Quantitative, Serum.
www.labcorp.com 2003. Ref Type: Internet Communication.
5. Minodora Dobreanu. Metabolismul proteinelor. În Biochimie clinică. ImplicaŃii practice. University Press, România, Ed. 2006, 133-150.